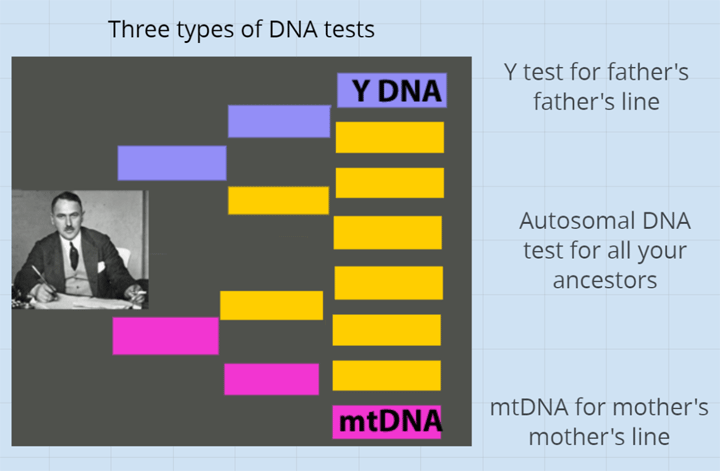
Sunday April 25 is DNA Day. Every major company is having a sale to celebrate. Family Tree DNA is even having sales on the upgrades to their various Y tests. This is a great opportunity to get that done. Click here for their price list.
Click the image below for a very interesting post on the history of DNA day from the 23andme blog.
There has been much exciting news in the genetic genealogy world while I was away (I still am on a break). So here are some of the announcements you might want to read about.
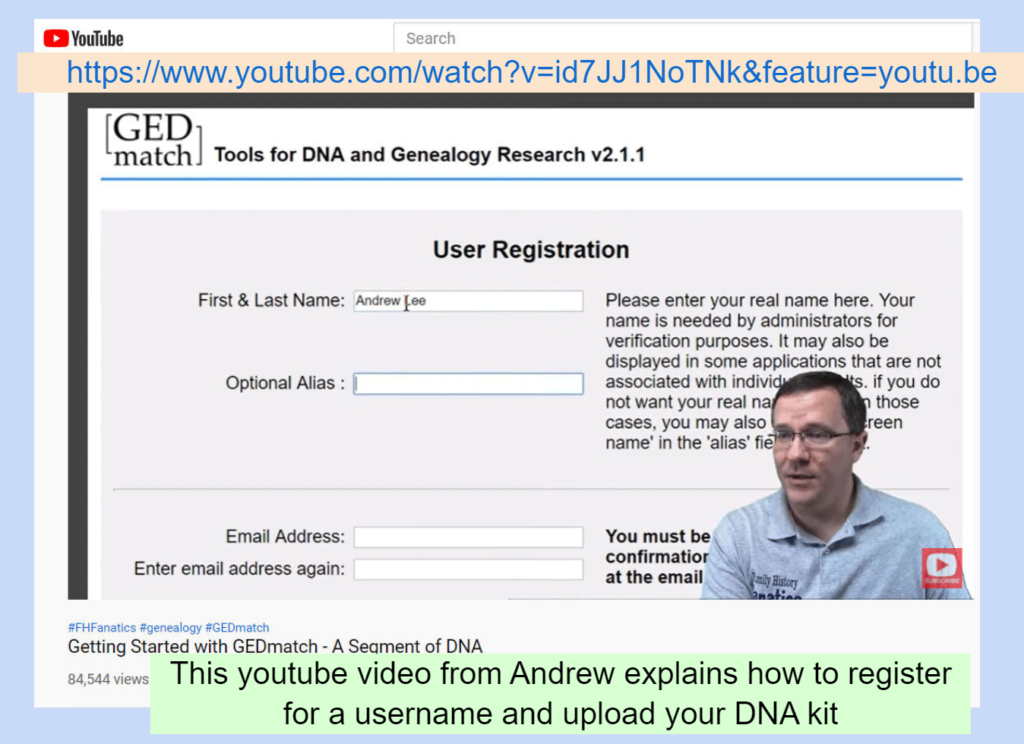
- GEDmatch has collaborated with Genetic Affairs to improve their clustering tools and to include auto-tree building. Click here for that news release. The next blog post I intend to write will evaluate these.
- DNApainter is sending out a free monthly newsletter, the most recent had information about a couple of new releases. Go to that site and click the green banner at the top of the homepage to sign up if you’re interested.
If you haven’t tried Deep Nostalgia, the new tool to animate family photos at MyHeritage, maybe click here to read all about it.
Ancestry has reorganized their Match list page. More of your notes will now show up since they have been moved to be below each match.