I suddenly realized that I could find the people who match my late husband Steven M Cooper on his mutated section of the BRCA2 gene at the various DNA testing sites that show chromosome information. His particular BRCA2 mutation, implicated in breast cancer and melanoma, likely contributed to the fatal outcome of his prostate cancer. A problem with doing this is that none of his tested family members match that gene, so there would be no way to know if his matches had his bad maternal BRCA2 or his good paternal one.
So should I contact those many people and warn them? I had previously alerted his known LILIEN side cousins to this issue and already a second cousin once removed on his LILIEN line discovered her breast cancer early due to my warning. However I may be sending a false alarm to many. I decided it was something I should do. My family history investigations left me confident that Steve’s mutation came from one of the the parents of his grandmother Amalie LILIEN Tieger (jewish) born in Kalusz, Ukraine. Of course, it may well have originated further back.
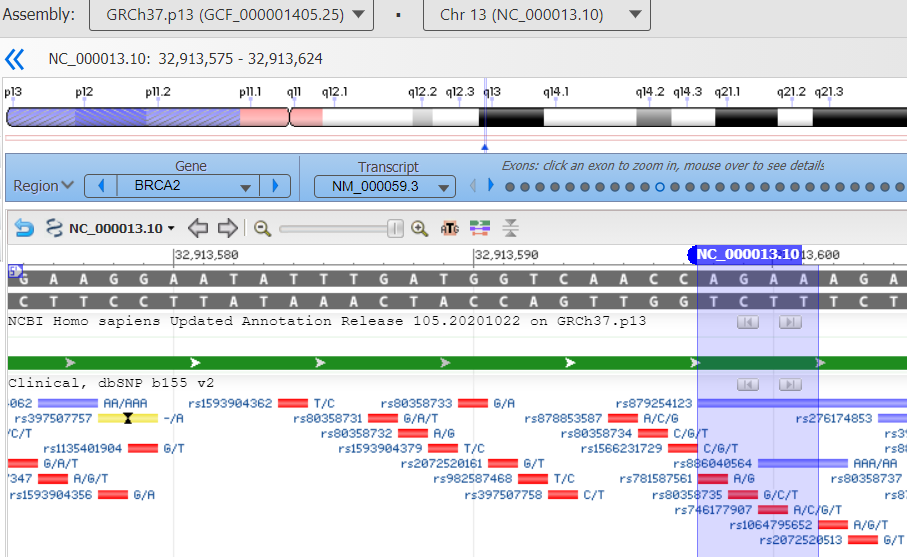
First I had to locate the mutation in a numbering system that would translate to what we get from our DNA testing companies. From various google searches I learned that BRCA2 is located on chromosone 13. Looking at the report from Color Genomics, the test his oncologist ordered, I could see the location was a deletion at base pairs 32,913,602_32,913,605. More googling found that this is not the common Jewish BRCA2 mutation. That explains why his initial 23andme test years ago did not find it. Next I found the actual National Health Institute fact sheet for his mutation (click here) which had a click point to the diagram below. Click here for the cancer.gov discussion of BRCA2
Now to find the people who match him on that segment. I downloaded the full list of his matches with segment information from each site. The easiest site to use was GEDmatch because I could use the segment search function to get just the matches to his BRCA2 section of chromsome 13. At the other sites I had to get the full list of all matching segments and then sort by chromosome and start point to find the matching people.